CAMPYLOBACTER IN SHEEP > VIDEO
Listen to this audio from the Head Shepherd podcast series to learn about Campylobacter, how its spread, and how to prevent and manage it.

CAMPYLOBACTER IN SHEEP > FACT-SHEET
ABOUT THIS PODCAST
This podcast was produced as part of neXtgen Agri’s Head Shepherd Podcast series. Covering all things livestock through the amazing stories of farmers and the people that study them. Allflex and MSD Animal Health are a proud sponsor of the series and we highly recommend you have a listen to more of the podcasts.

For more visit: www.nextgenagri.com/head-shepherd-podcast
WHAT IS CAMPYLOBACTER?
- Campylobacter is a bacteria and is one of the most commonly diagnosed causes of infectious abortions of ewes in New Zealand. Other commonly diagnosed causes are Toxoplasmosis and Salmonellosis.
- It is generally associated with abortions in the last 6 weeks of pregnancy, however trial work has shown it causes pregnancy losses at other times when the losses are not as easy to see (eg embryonic loss, resulting in dry ewes or late lambers).
- It can also cause stillbirths or the birth of weak lambs that die soon after birth.
- There are different strains, the two most prevalent in NZ sheep are:
- C. fetus fetus
- C. jejuni
- 88% of NZ farms have Campylobacter present.1

Diagnosed Sheep Abortion Cases
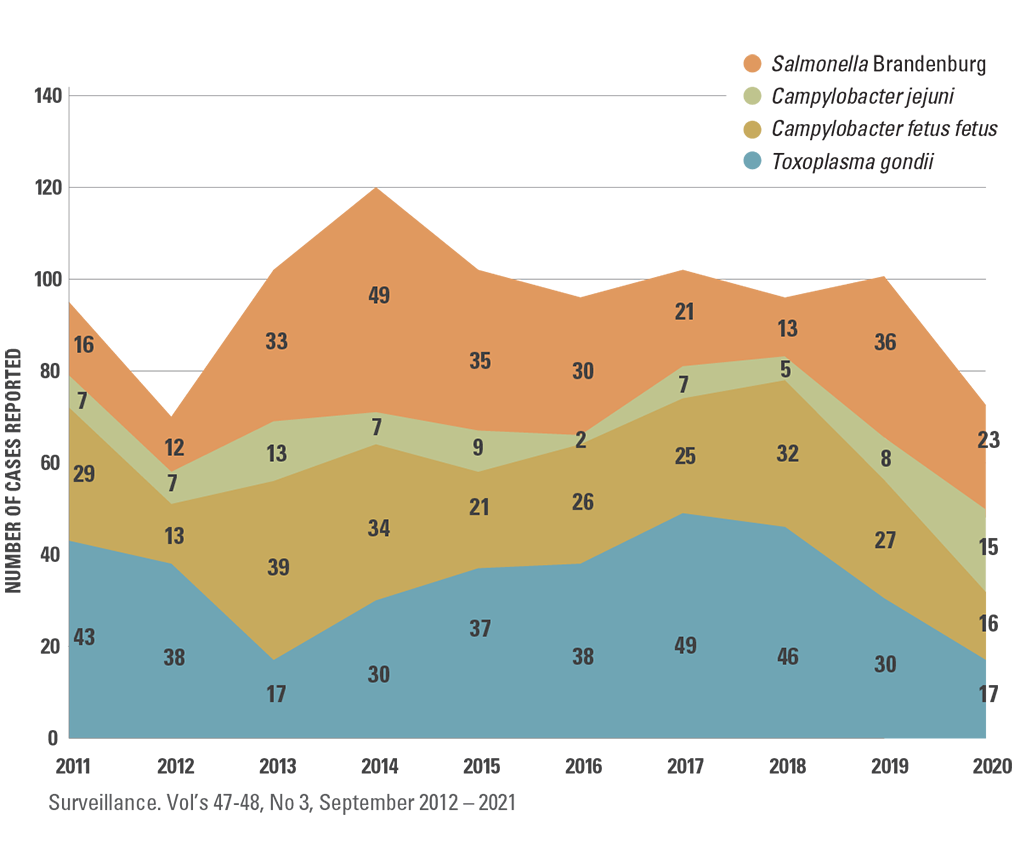
HOW IS CAMPYLOBACTER SPREAD?
- Campybacteriosis spreads when susceptible animals ingest contaminated feed or water, or by direct contact with infected fetuses or foetal membranes.
- Post infection, the organism is present in discharges for up to 6 weeks, with some ewes becoming long term carrier between seasons.2
- Infection can persist on a farm for a number of years in carrier sheep which cannot be identified.
CAMPYLOBACTER VACCINATION
- Campyvax4® is the only Campylobacter vaccination for sheep in New Zealand.
- It contains four strains of Campylobacter: 3 x C. fetus fetus and 1 x C. jejuni.
- For prevention, in the first year of use two shots of the vaccine should be given 4-8 weeks apart, with the 2nd booster shot ideally given prior to mating.
- In subsequent years a single shot (annual booster) should be given prior to mating for ongoing protection.

BENEFITS OF PREVENTATIVE VACCINATION WITH CAMPYVAX4®
- Prevents significant losses due to abortion storms.
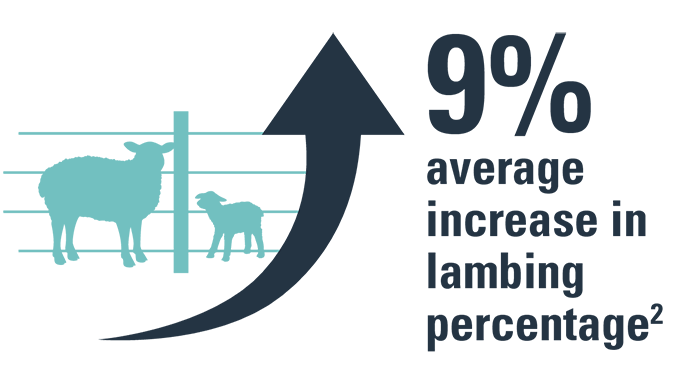
- Increases lambing percentage by an average of 9% even in farms that do not see abortions.3
- Protection against losses of weak, non-viable lambs.
MANAGING AN OUTBREAK
During an outbreak the focus should be on preventing access of animals to infection by limiting the spread through:
- Reducing stocking density
- Removing stock from contaminated pasture
- Strict adherence to hygiene practices
NOTE: These control measures are very hard to implement on a busy commercial farm.

REFERENCES
- Dempster, RP, Wilkins, M, Green, RS & de Lisle, GW (2011) Serological survey of Toxoplasma gondii and Campylobacter fetus fetus in sheep from New Zealand, New Zealand Veterinary Journal, 59:4, 155-159
- West, DM, Bruere AN & Ridler AL (2017) The Sheep: Health, Disease & Production page 64
- Anderson, P (2001) The implications of Campylobacter Infections in Ewe Flocks. Proc 31st Annual Seminar, Society of Sheep and Beef Cattle Veterinarians., NZVA p31-40
- Sahin, O, Yaeger, M, Zuowei, W and Zhang, Q. (2017) Camylobacter-Associated Diseases in Animals. The Annual Review of Animal Biosciences. 5: 9.1-9.22
Surveillance Vol’s 47-48, No.3, September 2012-2021
FOR MORE:
Or find us on YouTube by searching: TopFarmersNZ
Or visit: soundcloud.com/TopFarmers
Or visit: msd-animal-health.co.nz

Top Farmers Know-How provides a reference library of industry best practice in some key animal health management areas including mastitis, dry off, calf health, BVD, salmonella and campylobacter. We know that farmers and vets are busy people, so we’ve created resources in different formats and in bite-sized chunks to make it more flexible and accessible.
